Copper Life Cycle
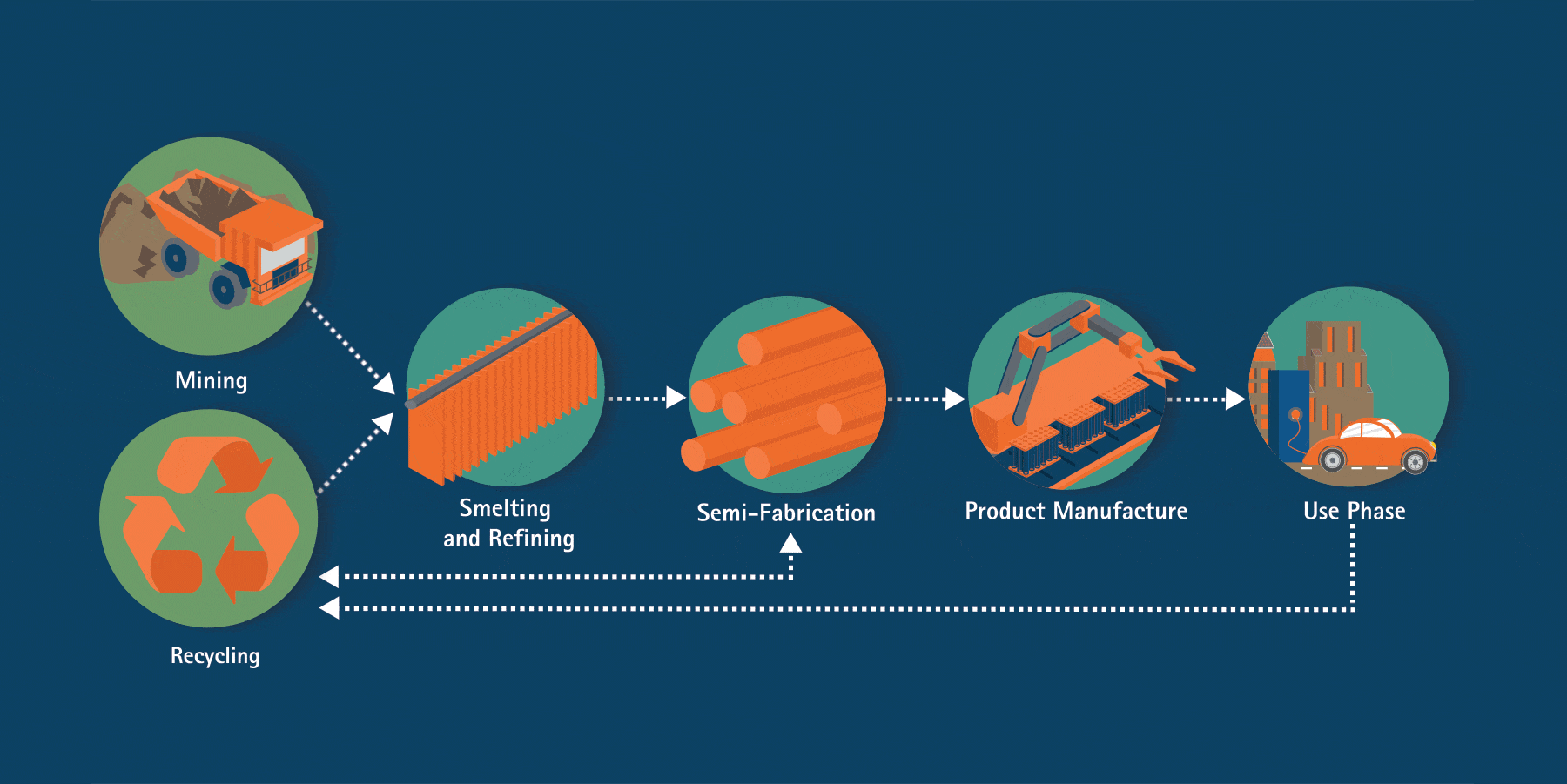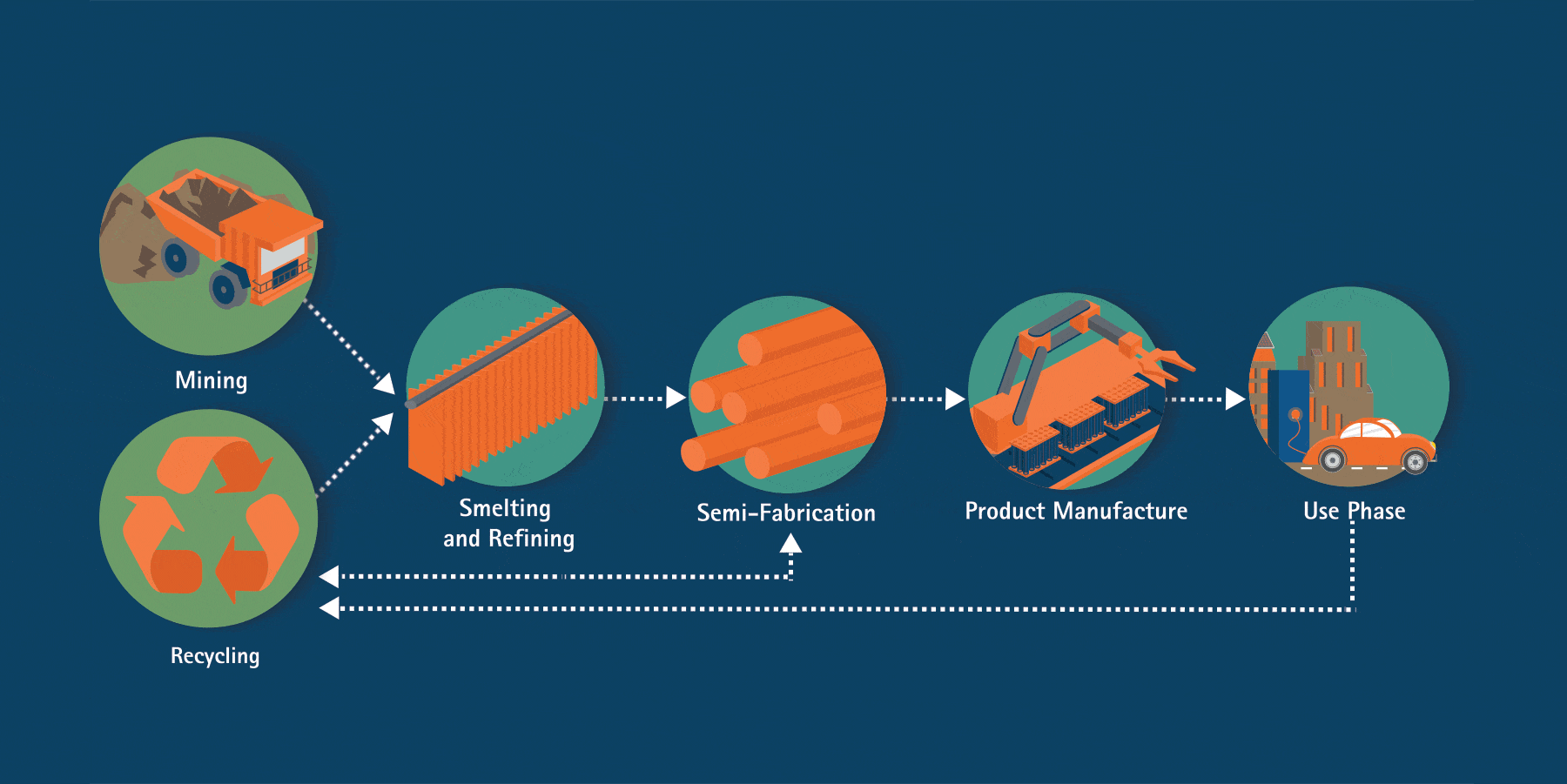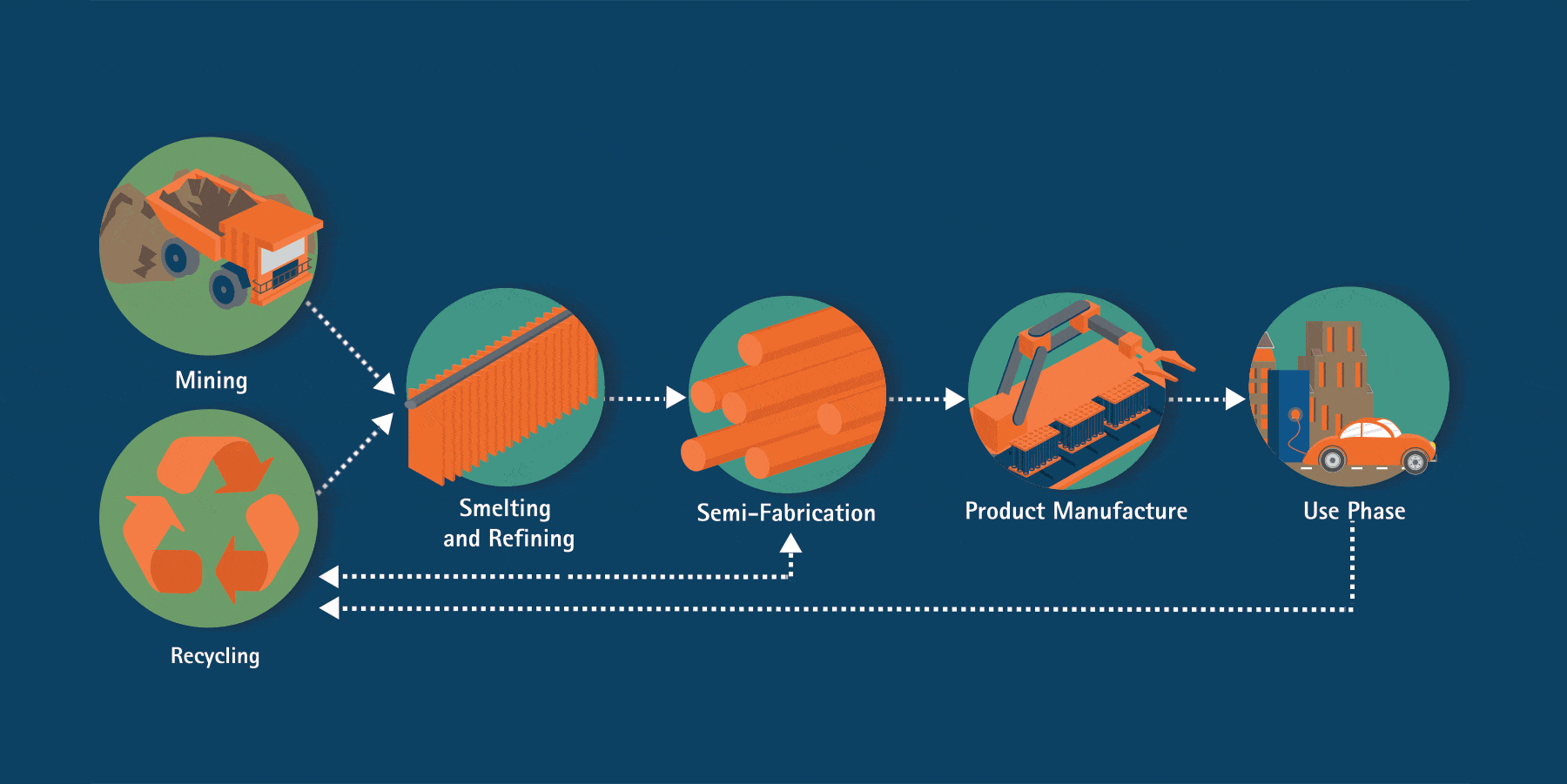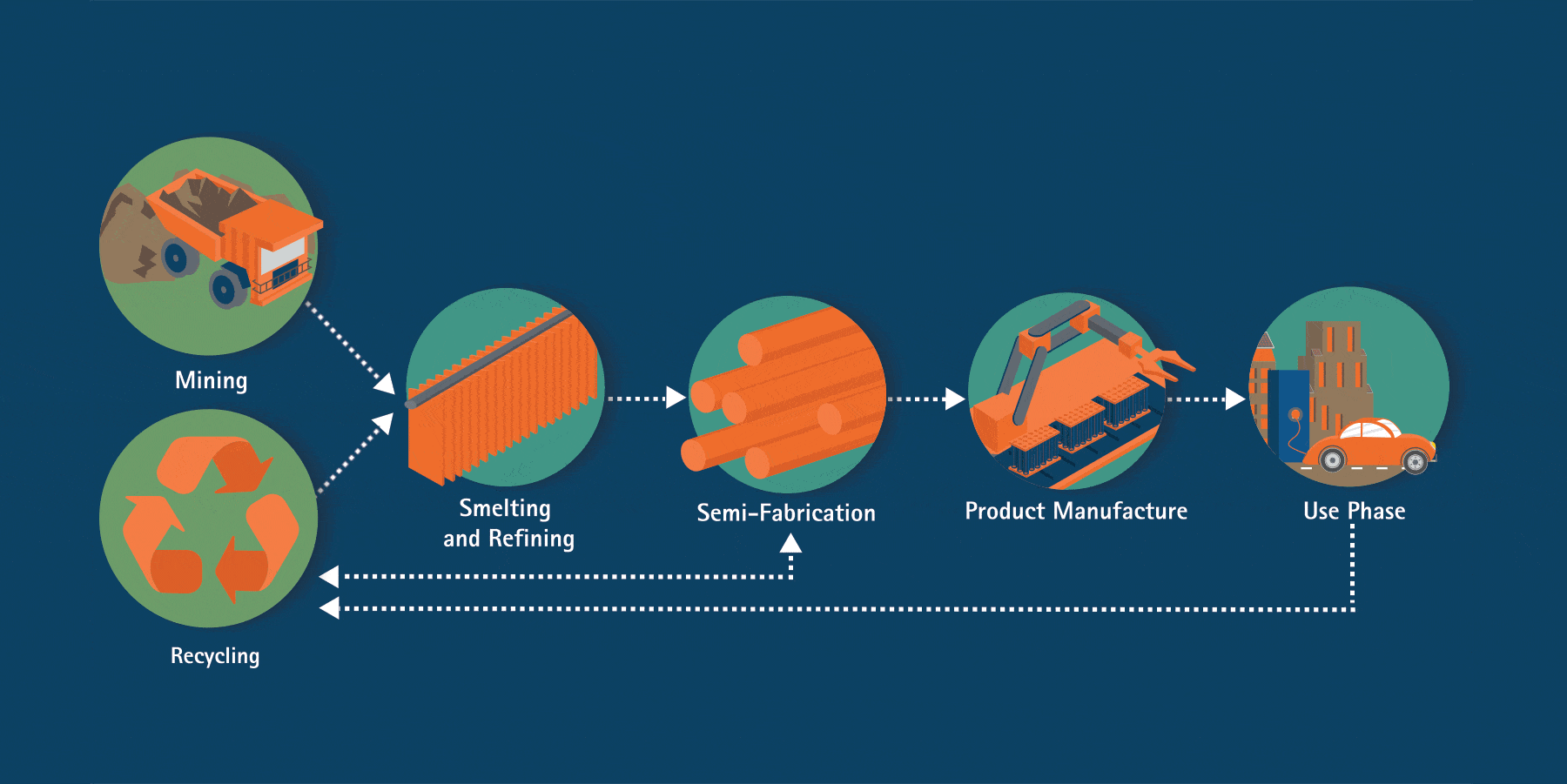
From its original home in the earth’s crust, copper passes through several stages to reach a long life in essential products like electronics, appliances, electrical grids, vehicles and renewable energy technologies. As a 100% recyclable material, copper can be reused over and over again with no loss to its physical properties.
The material produced from ores and concentrates is referred to as primary copper production. Secondary copper can also be produced by recycling scrap, as well as finished products, and has the same performance properties as primary material.
Learn more about this renewable resource’s life cycle

Copper Recycling
During the last decade, more than 30 percent of annual copper use came from recycled sources. Based on the global copper stocks and flows model, recently developed by the Fraunhofer Institute, it is estimated that two thirds out of the 550 million tonnes of copper produced since 1900 are still in productive use (Glöser, 2013).

Mining
Primary copper production starts with the extraction of copper-bearing ores. There are two basic ways of copper mining: surface and underground mining. Due to copper being spread in relatively low concentrations over large areas, surface, or open-pit mining, is the predominant mining method for copper in the world.
Smelting and Refining
After mining, copper is produced by one of two process routes, pyrometallurgical (dry) or hydrometallurgical (wet). Smelting is a process of heating and melting ore to extract a metal like copper. Refining refers to any process that increases the grade or purity of the metal. After completing refining processes, copper cathode is generally 99.9 percent pure.
Semi-Fabrication
During semi-fabrication, copper, along with clean scrap, is converted into wire/rod, tubes, sheet and strips for use down the value chain.
Product Manufacture
Copper wire/rod, tubes, sheet, and strips are transformed into finished products that can be used directly by consumers and businesses.
Use Phase
Nearly 28 million tonnes of copper is used annually. The majority of copper produced worldwide (70 percent) is used for electrical/conductivity applications and communications.

There’s more copper available than ever before.
Learn more about meeting demand with primary and secondary copper.
