The European Copper Institute (ECI) supports the EU’s climate ambitions for 2030 and 2050. Ambitious policies are needed to increase electrification, the deployment of renewables and energy efficiency to decarbonise the European economy and reduce dependency on Russian fossil fuels.
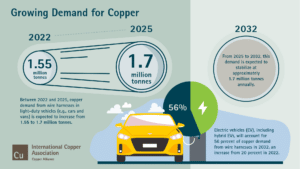
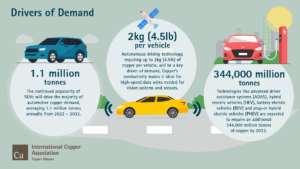
Copper is a crucial raw material for electrification and for the energy transition at large: it is the one non-ferrous metal used in all the main decarbonisation technologies today.More copper will therefore be needed in the coming years to enable the decarbonisation of the economy.
As an energy intensive industry, the copper producers that we represent in Europe are taking steps to decarbonise their production sites and are committed to working towards carbon neutrality by 2050. Copper producers today face the twin investment challenge of increasing production to meet the needs of the energy transition, while also investing to lower the environmental and carbon footprint of copper production.
In Europe, unprecedented energy prices are increasing the operational costs of copper smelters and refiners, and causing a competitive disadvantage vis-à-vis producers in other regions where energy prices remain lower. Access to affordable renewable and low-carbon electricity is a pre-requisite for decarbonising copper production. In the current context, this is a key concern for the industry.
We welcome the underlying idea behind CBAM to introduce a level playing field for carbon costs between EU and non-EU producers, which would allow phasing out the current carbon leakage protection measures under the EU Emission Trading System (ETS). In practice, however, several important concerns remain as to the ability of CBAM to establish a real level playing field, in particular in relation to the treatment of EU exports, the inclusion of indirect emissions, circumvention and the on-the-ground application of CBAM.
Copper is not included in the list of sectors to which CBAM will apply in the first instance. However, we note the intention of the EU institutions to expand CBAM to other ETS sectors in the future. In this regard, we are deeply concerned by the approach of the European Parliament that would mandate the application of CBAM to all ETS sectors by 2030 and empower the Commission to extend the scope of CBAM through delegated acts. The extension of CBAM to new sectors cannot be automatic and must be subject to impact assessments for each new sector. The extension into new sectors must also follow the ordinary legislative process to allow industry and other stakeholders the opportunity to engage in the decision-making process.